In the dynamic realm of IT security, safeguarding your endpoints isn’t merely a precaution—it’s imperative. For organizations leveraging Power Automate, the convenience of HTTP request triggers can expose vulnerabilities unless properly secured. This guide explains how Microsoft’s enhanced security options fortify your workflows against unauthorized access.
New Security Features in Power Automate
Power Automate has introduced refined settings that control who can trigger your HTTP request flows, significantly enhancing security:
- Any User in My Tenant: This setting restricts flow access to your organization’s users, requiring them to authenticate with a valid user token.
- Specific Users in My Tenant: This more granular option allows you to designate specific users within your tenant who are authorized to trigger the flow.
These enhancements ensure that only verified users can execute flows, thus protecting your systems.
Setting Up Application Registration
1. Register a Client Application in Microsoft Entra ID
- Navigate to the Azure Portal: Open Azure Active Directory from the portal.
- Create a New Application: Select ‘App registrations’ > ‘New registration’. Fill in necessary details such as name and redirect URI.
2. Obtain Application ID and Tenant ID
- After registering, note the Application ID and Tenant ID provided on the overview page.
3. Generate a Client Secret
- Go to ‘Certificates & secrets’ and create a new secret. Choose an expiration period and record the secret safely.
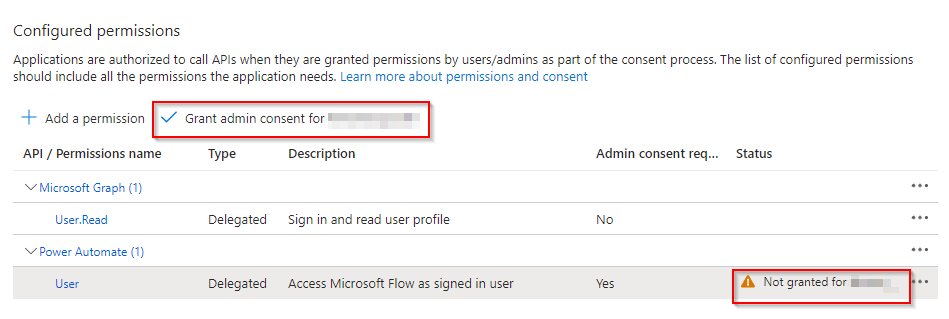
4. Configure API Permissions
- Under ‘API permissions’, add necessary permissions for Microsoft Power Automate API. Ensure to get admin consent for these permissions.

Implementing Secure Triggers
Scenario 1: From Within a Flow
- Configure Authentication: In your Power Automate flow, add an HTTP action. Set the authentication to “Active Directory OAuth” and input your Tenant ID, Client ID, and the specified Audience.

Scenario 2: From a Plugin
- Obtain an access token using client credentials first, then use this token as a bearer token to authenticate your HTTP request. This method integrates securely with Dynamics 365 plugins.
Sample Code for Plugin Execution:
private const string TenantId = "00000000-0000-0000-1111-000000000000";
private const string ClientId = "00000000-0000-2222-0000-000000000000";
private const string ClientSecret = ""; // Replace with your secret
private const string Authority = "https://login.microsoftonline.com/";
private const string Scope = "https://service.flow.microsoft.com//.default";
private const string FlowUrl = "https://prod-25.australiaeast.logic.azure.com:443/workflows/efc626b5efd0ec11a7b6002248180d15/triggers/manual/paths/invoke?api-version=2016-06-01";
private async Task CallFlowAsync(ITracingService tracingService)
{
try
{
// Acquire the access token
string accessToken = await GetAccessToken(tracingService);
// Make the HTTP request to the Power Automate flow
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Bearer", accessToken);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
var content = new StringContent("{ \"message\": \"Hello from Dynamics 365 Plugin!\" }", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
HttpResponseMessage response = await client.PostAsync(FlowUrl, content);
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
// Handle successful response
string result = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
tracingService.Trace("Flow executed successfully: " + result);
}
else
{
// Handle error response
string error = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
tracingService.Trace("Error executing flow: " + error);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
tracingService.Trace("Exception: " + ex.Message);
}
}
private async Task<string> GetAccessToken(ITracingService tracingService)
{
try
{
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
var parameters = new[]
{
new KeyValuePair<string, string>("grant_type", "client_credentials"),
new KeyValuePair<string, string>("client_id", ClientId),
new KeyValuePair<string, string>("client_secret", ClientSecret),
new KeyValuePair<string, string>("scope", Scope)
};
var content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(parameters);
HttpResponseMessage response = await client.PostAsync($"{Authority}{TenantId}/oauth2/v2.0/token", content);
string responseString = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var tokenResponse = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TokenResponse>(responseString);
return tokenResponse.AccessToken;
}
else
{
tracingService.Trace("Failed to acquire access token: " + responseString);
throw new Exception("Failed to acquire access token.");
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
tracingService.Trace("Exception in GetAccessToken: " + ex.Message);
throw;
}
}
Scenario 3: From JavaScript
- Utilize a custom API method connected to your plugin which handles the authentication and execution of the flow securely.
The introduction of refined security settings for HTTP triggers in Power Automate marks a significant advancement in safeguarding automated workflows. By following the outlined steps, you can ensure that your workflows are triggered securely, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of your automated processes.
