The Power Platform has come a long way from building basic canvas and model-driven apps. With the introduction of AI Copilots and natural language experiences, there’s a new frontier for makers and developers: integrating AI prompts directly into Dataverse through a Prompt Column.
In this post, we’ll dive into:
- What is a Prompt Column?
- How it works with AI Builder
- How to write effective AI prompts
- Scenarios and best practices
What is a Prompt Column?
A Prompt column is a new type of field in Dataverse that connects to AI Builder’s prompt engineering capabilities. It allows you to define LLM-powered prompts directly in a table just like you would define a text, number, or lookup field.
But instead of collecting data from a user, a prompt column generates its value dynamically, based on a custom AI prompt you write.
Essentially, you’re embedding AI into your data model.
How Does It Work?
- You define a prompt template (in natural language or structured prompt form)
- When a record is saved (or when the user triggers it), AI Builder evaluates the prompt
- The output is stored in the prompt column
- You can display this AI-generated insight in forms, views, or reports
Prompt columns support GPT-style large language models and are ideal for generating summaries, categorizations, tone detection, recommendations, and more.
Real-World Use Cases
| Scenario | Prompt Column Use |
|---|---|
| Customer Service Case | Summarize customer complaint in a formal tone |
| Sales Lead | Generate a follow-up email draft based on lead notes |
| Product Review | Classify tone as positive, negative, or neutral |
| Job Application | Recommend next steps for recruiter |
| Project Update | Extract action items from meeting notes |
Imagine not needing to build a Power Automate flow, custom plugin, or Copilot Studio topic just to generate insights it’s now a column type.
How to Create a Prompt Column
- Go to the table designer in Power Apps Maker portal
- Click + New column
- Select Prompt (Preview) as the column type
- Give it a name (e.g.,
summaryPrompt) - Enter the AI prompt template, this is where the magic happens
How to Write an AI Prompt (The Right Way)
According to Microsoft’s official guidance, writing a great prompt involves:
1. Be Specific
Tell the model what to do and how.
❌ “Summarize this text”
✅ “Summarize the customer issue in a polite and professional tone for an internal support ticket”
2. Use Placeholders for Fields
Prompt templates can include dynamic values from the same record.
Example:
Summarize the following case description into a single sentence: {caseDescription}
You can reference any other column using {columnLogicalName}. These are replaced at runtime with the actual record values.
3. Set the Tone or Format
Be explicit if you want a list, a paragraph, or even JSON.
- “Return a list of key tasks extracted from: {meetingNotes}”
- “Summarize the product feedback from {customerName} in a positive tone”
- “Output a JSON object with keys ‘sentiment’ and ‘recommendation'”
4. Avoid Open-Ended Ambiguity
AI models are powerful, but ambiguous prompts lead to unpredictable results.
❌ “What do you think about this?”
✅ “Based on {customerFeedback}, assess the sentiment as Positive, Neutral, or Negative”
Prompt Column Behavior and FAQs

Best Practices for Using Prompt Columns
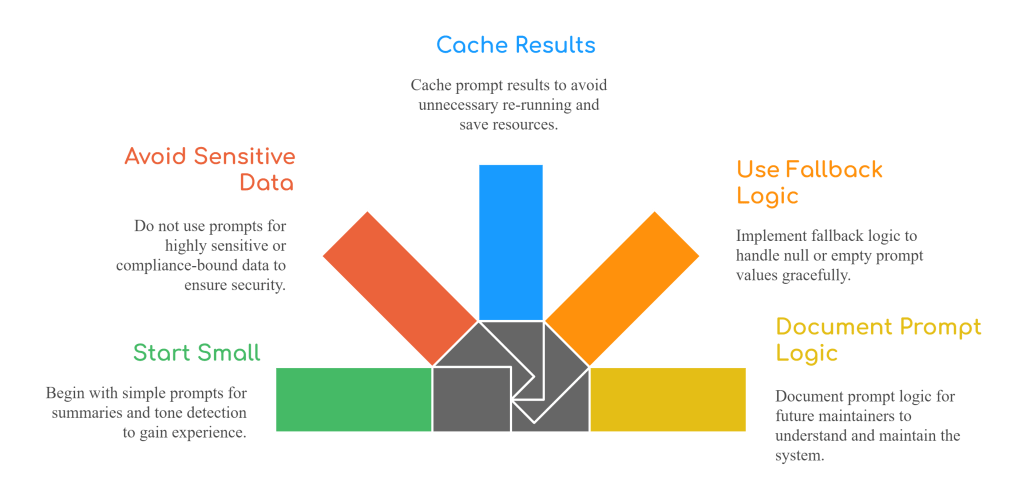
AI Inside the Table
Prompt columns represent a paradigm shift in how we think about data modeling in the Power Platform. It’s no longer just about storing and relating data it’s about infusing intelligence into the data model itself.
With just a few clicks and a prompt, you can add summarization, classification, and natural language understanding right inside Dataverse no flows, no plugins, no APIs.
This is low-code AI, done right.
