In Part 1, we explored the why and how of Azure integration with Dataverse using Service Bus and Azure-aware plug-ins.
Now in Part 2, we zoom into the real-world mechanics of working with Dataverse data inside Azure solutions. Whether you’re building APIs, serverless workflows, or batch processes this post is your launchpad.
Why Move Data from Dataverse to Azure?
Integrating Dataverse with Azure opens the doors to:
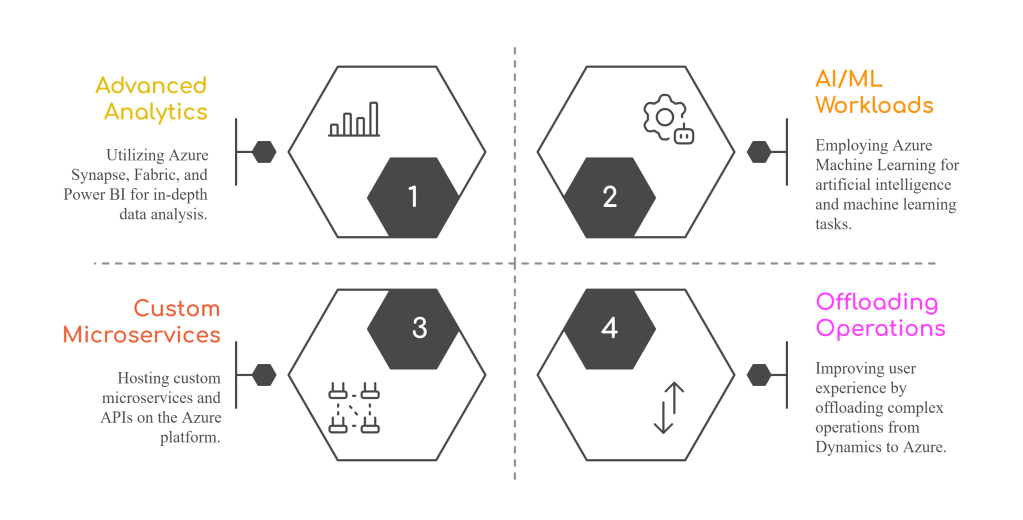
🧰 Your Integration Toolkit
Here are four ways you can access and work with Dataverse data in Azure:
1. Dataverse Web API – Direct, Fine-Grained Control
The Dataverse Web API is an OData v4-compliant RESTful API that enables direct access to all standard and custom tables in Dataverse. Azure services like Azure Functions, Logic Apps, or even custom APIs can use this API to:
- Perform CRUD operations (
Create,Read,Update,Delete) - Execute FetchXML queries or filtered data retrieval
- Run bound/unbound actions and functions
- Trigger business rules or plug-ins if needed
🔐 Authentication:
Use Azure AD app registration to get tokens via client credentials or managed identity (if calling from Azure-hosted services).
🧪 Example Scenario:
An Azure Function calls the Web API every hour to pull open opportunities and generate a predictive score using Azure ML, updating back the probability score field.
2. Azure Data Factory – Bulk Movement at Scale
Azure Data Factory (ADF) supports Dataverse as a source and sink via the OData connector. It’s best for scheduled, high-volume data movement tasks.
- Load large datasets from Dataverse to Azure Data Lake or SQL
- Transform data using mapping data flows
- Use copy activities to move data between environments or storage accounts
📅 Use When:
- You’re building nightly data warehouse loads
- You want to extract full tables or delta changes
⚠️ Gotchas:
- Make sure API throttling limits are considered (use pagination + retry policies)
- Column option set values are returned as integers (you may need transformation mapping)
🧪 Example:
Nightly job copies account and contact tables from Dataverse to Azure Data Lake for downstream Power BI reporting.
3. Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse – Near Real-Time Analytics
Synapse Link provides a near real-time sync from Dataverse to Synapse or Azure Data Lake without code.
- No need to write ETL pipelines
- Data is automatically kept in sync using change tracking under the hood
- Great for joining Dataverse data with other enterprise data sources
🚀 Ideal For:
- Analytics teams who want T-SQL or Spark access to Dynamics data
- Data fusion across ERP, CRM, and other sources
🧪 Example:
Sales and customer interaction data from Dataverse is streamed into Synapse. Analysts use it to build Power BI dashboards for executive decision-making.
4. Azure Functions + Service Bus – Event-Driven Custom Workflows
You can use Azure-aware plug-ins to send execution context (via IPluginExecutionContext) to Azure Service Bus when a record is created/updated/deleted.
- Azure Function listens to that queue and processes the message
- Great for integrating with external APIs, or doing asynchronous processing
- Keeps plugin logic clean and offloads heavy lifting to Azure
⚙️ Setup Includes:
- Registering a Service Endpoint in the Plugin Registration Tool
- Writing a plugin that posts data to the queue
- Azure Function app with Service Bus trigger
🧪 Example:
On every new lead in Dynamics 365, an Azure-aware plugin posts to Service Bus. A Function picks it up, enriches with external company data (e.g., via Clearbit API), and updates the record back in Dataverse.
🧩 Design Considerations
- Security: Use Managed Identity or Azure AD to authenticate Azure services with Dataverse.
- Throughput: Be aware of API limits and throttling when pulling large volumes.
- Data Modeling: Normalize or flatten your data depending on the analytics engine you’re targeting.
- Latency: Choose real-time (webhook/Azure Function) vs. batch (ADF/Synapse) based on the use case.
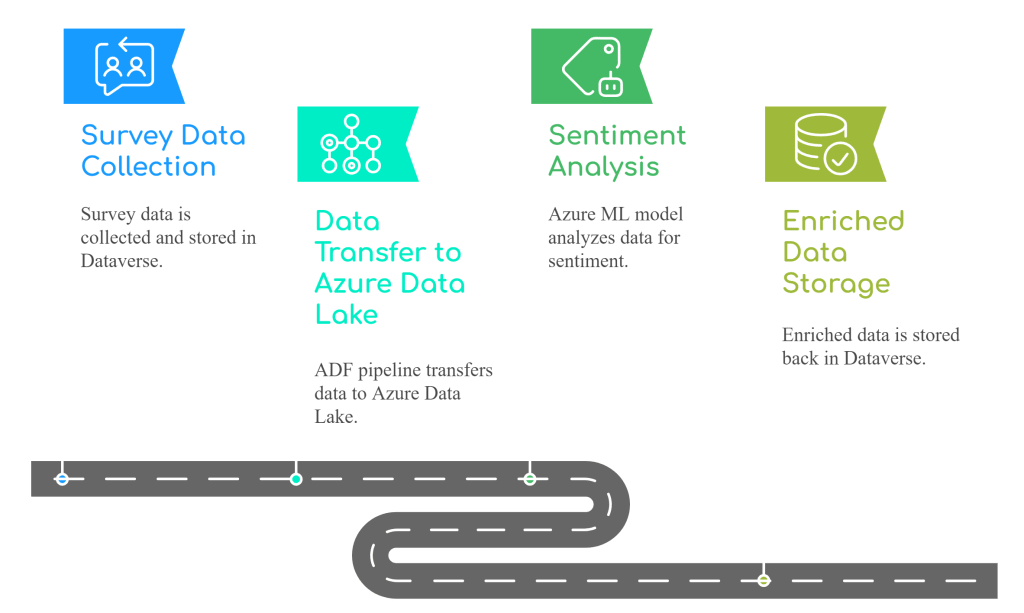
Sample Scenario
Use Case: Customer satisfaction survey results are collected in Dataverse and analyzed using Azure ML.
Flow:

One thought on “Working with Dataverse Data in Azure – Practical Patterns & Considerations”