In previous posts, we used the default indexing behavior of Dataverse. But what if your data needs custom tokenization, filters, or language handling?
Enter Custom Search Analyzers a way to control how your data is indexed and searched.
What Are Search Analyzers?
Search analyzers define how text fields are:
- Tokenized (split into searchable pieces)
- Normalized (e.g., lowercased, stripped of diacritics)
- Filtered (e.g., stemming, stop words)
Why Customize?
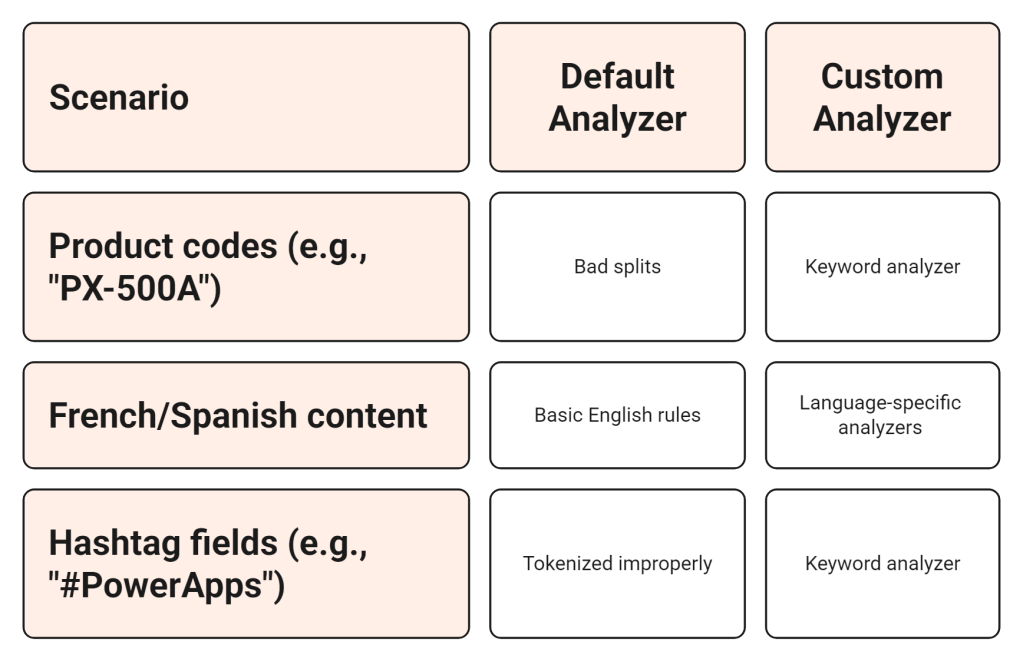
How to Define a Custom Analyzer
Custom analyzers are defined at the column level using the Web API or SDK. They are applied only to searchable text columns.
Example Request:
PATCH https://<env>.crm.dynamics.com/api/data/v9.2/EntityDefinitions(LogicalName='account')/Attributes(LogicalName='new_productcode')
Content-Type: application/json
{
"SearchAnalyzer": "Keyword"
}
Built-in Options
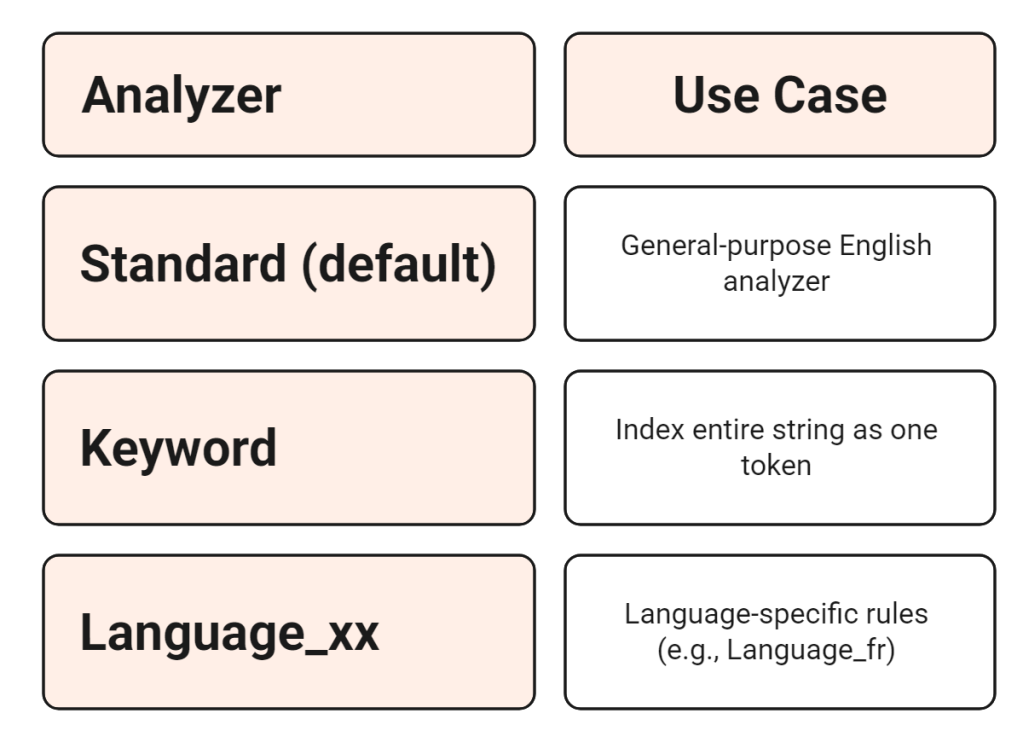
You can also set
SearchAnalyzerduring column creation.
Changing an Existing Analyzer
You must disable search, update the analyzer, then re-enable search on the column.
PATCH /Attributes(LogicalName='new_productcode')
{
"IsSearchable": false
}
Then update the SearchAnalyzer and re-enable IsSearchable: true.
Changing analyzers triggers a re-index of that column.
Testing Custom Analyzer Behavior
After applying a custom analyzer:
- Use the
SearchQueryAPI to see how terms are matched - Check token behavior using search suggestions
- Validate multilingual relevance where applicable
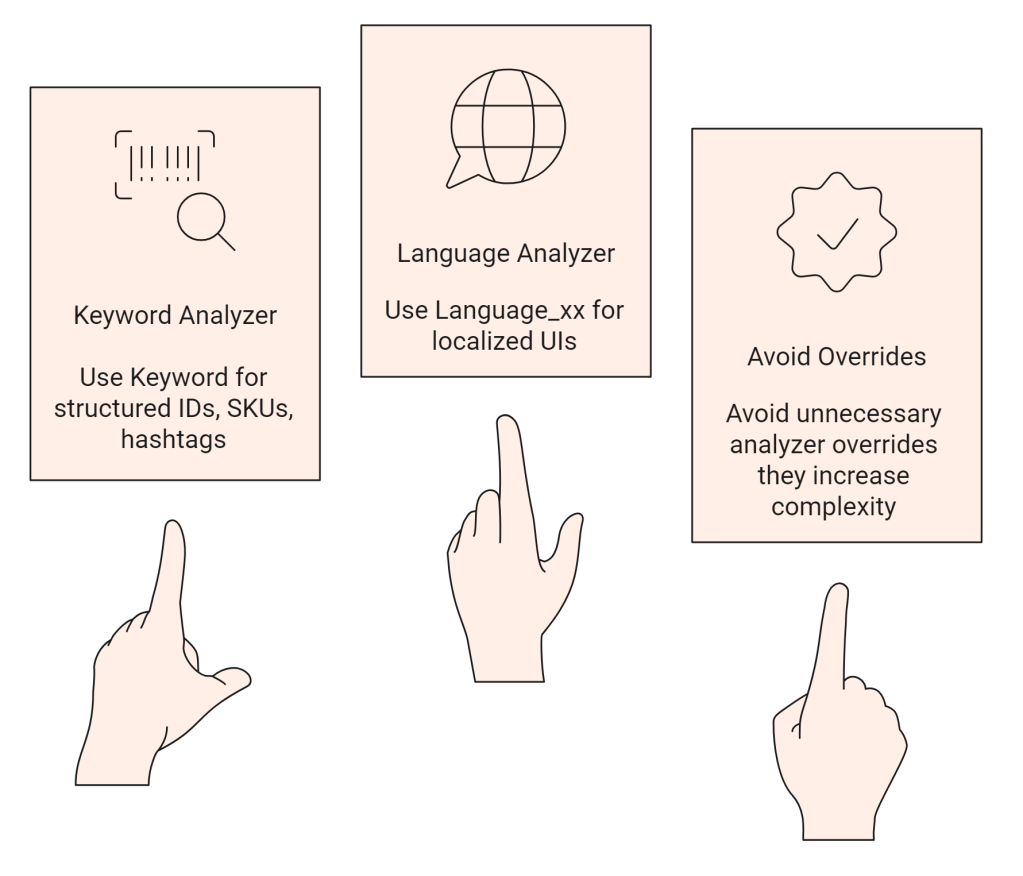
Best Practices
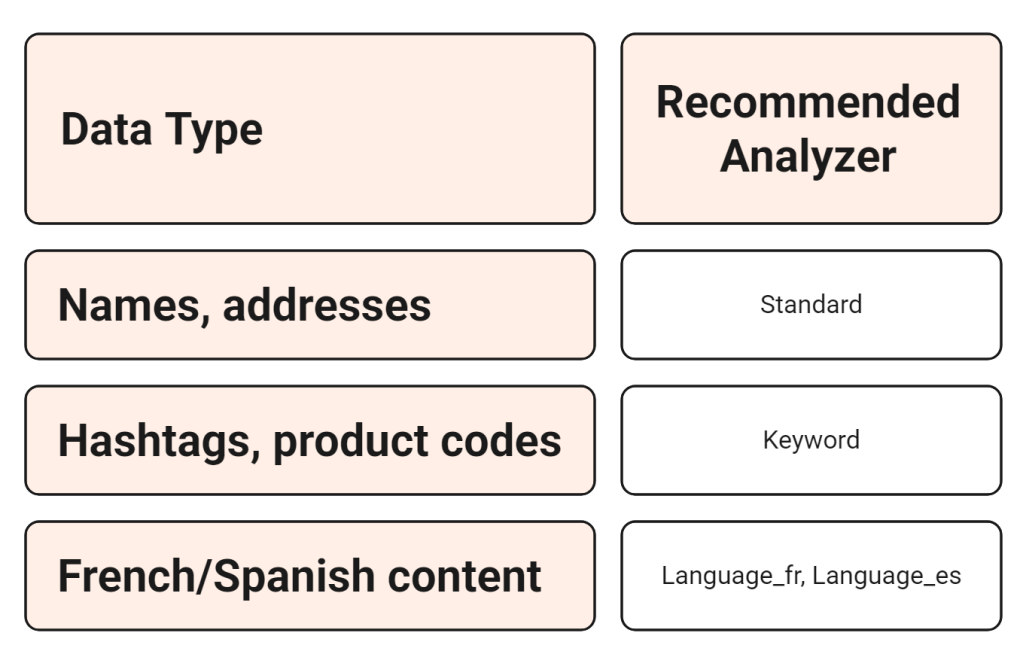
When to Use Custom vs Standard
Bonus Tip: Analyzer & Relevance
Changing the analyzer changes how ranking behaves e.g., exact matches may get higher weight with Keyword, while fuzzy matches benefit from Standard.
